Anatomy & Physiology: Muscles—Deltoid.
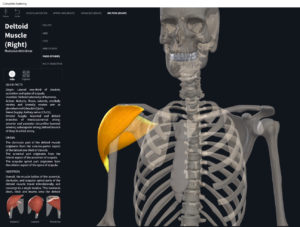
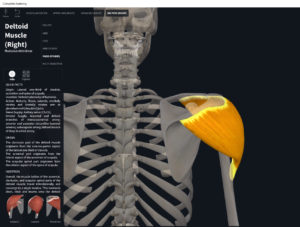
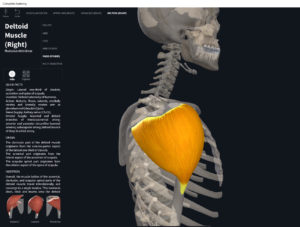
Structure.
- Origin: lateral 1/3 (acromial extremity) of clavicle.
- Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus.
Function.
- Concentric action: abduction at the glenohumeral (GH) joint. Arm flexion at GH joint (anterior deltoid). Medial rotation of the arm at GH (anterior deltoid). Horizontal flexion at the GH joint (anterior deltoid). Arm extension (posterior deltoid). Lateral rotation (posterior deltoid). Horizonal extension at GH (posterior deltoid).
- Reverse mover actions: downward rotation of scapula at glenohumeral and scapulocostal joints; ipsilateral rotation of the trunk; contralateral rotation of the trunk.
- Eccentric action: controls/restrains/slows arm adduction, extension, horizontal extension, flexion, horizontal flexion, lateral rotation, and medial rotation. Upward tilt of scapula such that inferior angle lifts off the thoracic wall.
- Isometric action: stabilization of the shoulder girdle. Stabilize clavicle.
- Innervation: axillary nerve.
- Arterial supply: anterior and posterior circumflex humeral arteries (branches of axillary artery). Pectoral and deltoid branches of thoracoacromial trunk (branch of axillary artery).
Clinical Significance.
More.
- https://www.anatomynext.com/muscles-deltoid/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K2wlYdMeJxU
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fx1alu8UThQ
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Cedars-Sinai. (2018). Vertebrae of the spine. Retrieved from https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/v/vertebrae-of-the-spine.html
Clark, M., Lucett, S., Sutton, B. G., & National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2014). NASM essentials of corrective exercise training. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.