Anatomy & Physiology: Muscles—Quadratus Lumborum.
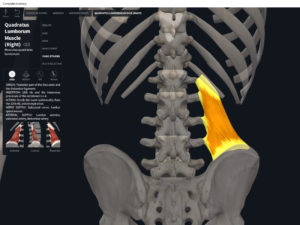
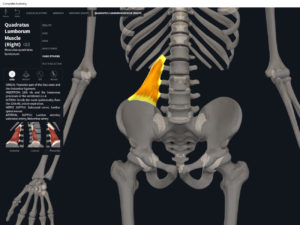
Structure.
- Origin: iliac crest, iliolumbar ligament.
- Insertion: 12th rib, transverse processes L2-L5.
Function.
- Concentric action: spinal lateral flexion; pulls rib 12 inferiorly during forced exhalation; fix ribs to prevent elevation during deep inhalation; help lumbar extension. Anterior pelvic tilt and lower spine extension relative to upper spine.
- Reverse mover action: trunk lateral flexion; rib 12 depression; trunk extension.
- Eccentric action: controls/restrains/decelerates contralateral and lateral spinal flexion; rib 12 elevation; ipsilateral depression and posterior tilt of pelvis.
- Isometric action: stabilization of the lumbo-pelvic-hip complex.
- Innervation: spinal nerves T12-L3.
- Arterial supply: branches of subcostal and lumbar arteries; iliolumbar artery.
Clinical Significance.
More.
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Cedars-Sinai. (2018). Vertebrae of the spine. Retrieved from https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/v/vertebrae-of-the-spine.html
Clark, M., Lucett, S., Sutton, B. G., & National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2014). NASM essentials of corrective exercise training. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.