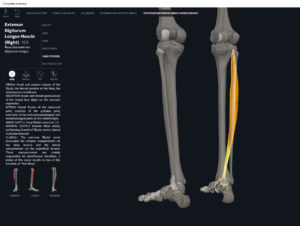
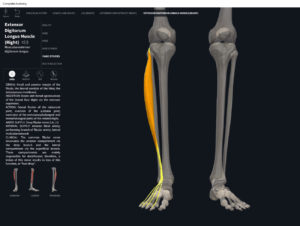
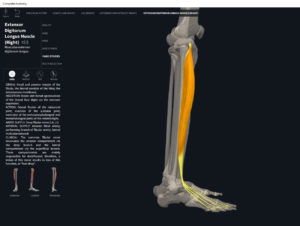
Anatomy & Physiology: Muscles—Extensor Digitorum Longus.
Structure.
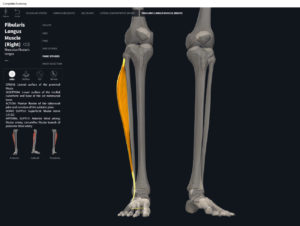
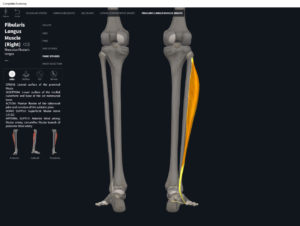
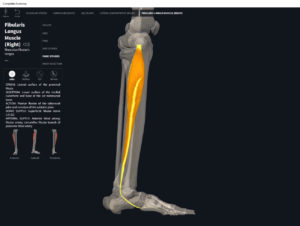
- Origin: lateral condyle of tibia, anterior fibula, interosseous membrane.
- Insertion: middle and distal phalanges of toes II-V.
Function.
- Concentric action: ankle dorsiflexion, extension of distal and middle phalanges of toes at interphalangeal joints and proximal phalanx of each toe at metatarsophalangeal joint.
- Reverse mover action: dorsiflexion; eversion/pronation of talus at subtalar joint; estend metatarsals at MTP joints and extension of the more proximal phalanges at the IP joints.
- Eccentric action: controls/restrains/decelerates flexion of toes 2-5 at MTP and IP joints; metatarsals 2-5 at MTP joints; plantarflexion; inversion/supination at subtalar joint.
- Isometric action: stabilizes ankle, subtalar and MTP and IP joints.
- Innervation: deep fibular (peroneal) nerve.
- Arterial supply: anterior tibial artery.
Clinical Significance.
More.
- https://www.anatomynext.com/extensor-digitorum-longus/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8j8nziP2SPU
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4WZbUAH5rH8
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WUS5BUB3fgM
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Clark, M., Lucett, S., Sutton, B. G., & National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2014). NASM essentials of corrective exercise training. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.