PCR stands for “polymerase chain reaction”. It was discovered in the 1983 by Kary Mullis. PCR is a technique that is used to create a whole bunch of copies (amplify) of a section of DNA or a gene for studying.
Download the high-quality poster here.
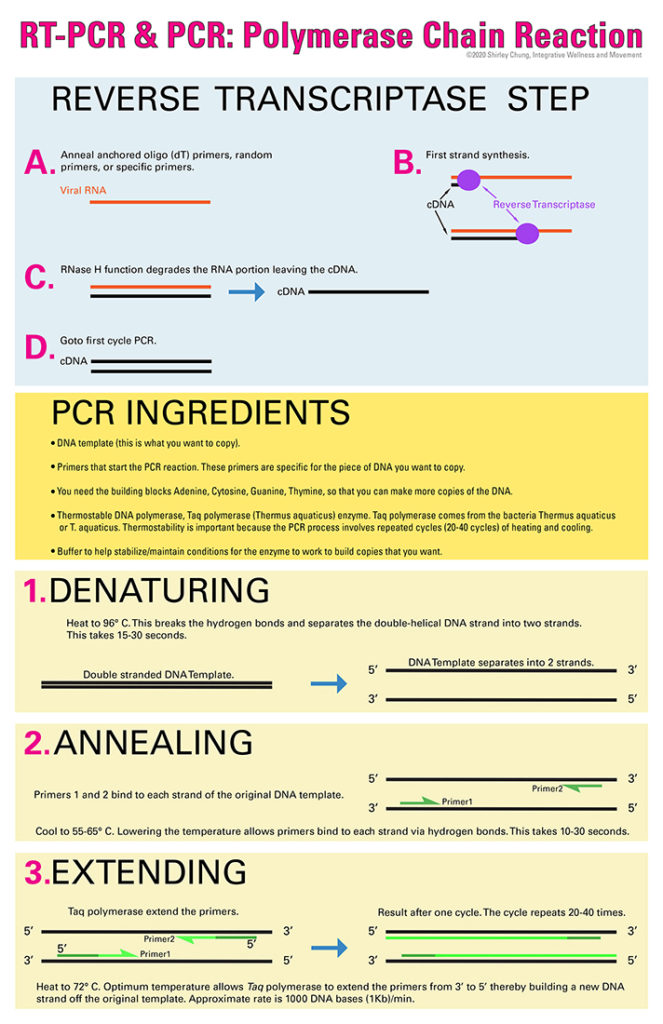
PCR “Recipe”
Ingredients:
- DNA template (this is what you want to copy).
- Primers that start the PCR reaction (on either side of the section of DNA you want copied). These primers are specific for the piece of DNA you want to copy.
- You need the building blocks which are the nucleotide bases (Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, Thymine) so that you can make more copies of the DNA.
- Thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase (Thermus aquaticus) enzyme. Taq polymerase comes from the bacteria Thermus aquaticus or T. aquaticus. Thermostability is important because the PCR process involves repeated cycles (20-40 cycles) of heating and cooling.
- Buffer to help stabilize/maintain conditions for the enzyme to work to build copies that you want.
Thermocycling (repeat steps 1-3, 20-40 times)
Step 1. Denaturing. Heat to 94-96 degrees C. The heat will help break the hydrogen bonds thus separating the two strands of DNA. This takes 15-30 seconds.
Step 2. Annealing. Cool to 50-65 degrees C. This allows the primers to bind to the individual strands of DNA via hydrogen bonding. This takes 10-30 seconds.
Step 3. Extension. Heat to 72 degrees C. The T. aquaticus bacteria is a heat-lover which allows it to withstand and function at higher temperatures. Taq polymerase attaches to primers and then adds bases, one-at-a-time, from the 5′ to 3′. The approximate rate is 1000 DNA bases (1Kb, kilobase) per 1 minute.
Other types of PCR
- Real-Time PCR (quantitative PCR or qPCR)
- Reverse-Transcriptase (RT-PCR)
- Multiplex PCR
- Nested PCR
- High Fidelity PCR
- Fast PCR
- Hot Start PCR
- GC-Rich PCR
- Long-range PCR
- Arbitrary Primed PCR
- Litigation-mediated PCR
- Methylation-specific PCR
- Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTR) PCR
- Asymmetric PCR
- Quantitative PCR
- Hot-start PCR
- Touchdown PCR
- Assembly PCR
- Colony PCR
- Digital polymerase chain reaction
- Suicide PCR
- COLD-PCR
Continue to read about RT-PCR.
References
