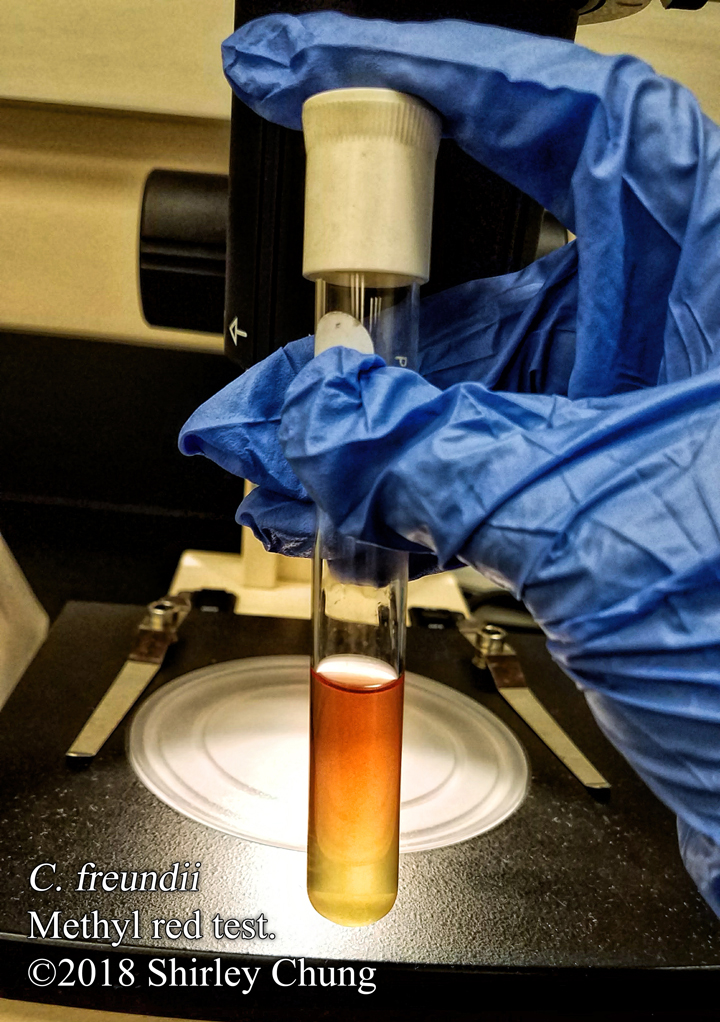
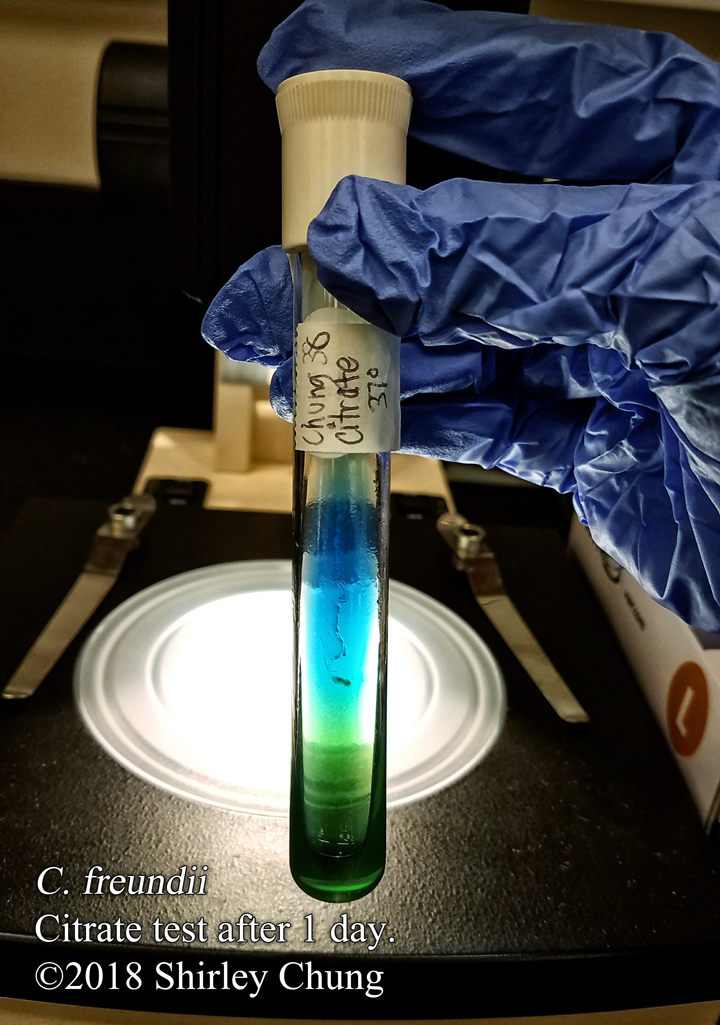
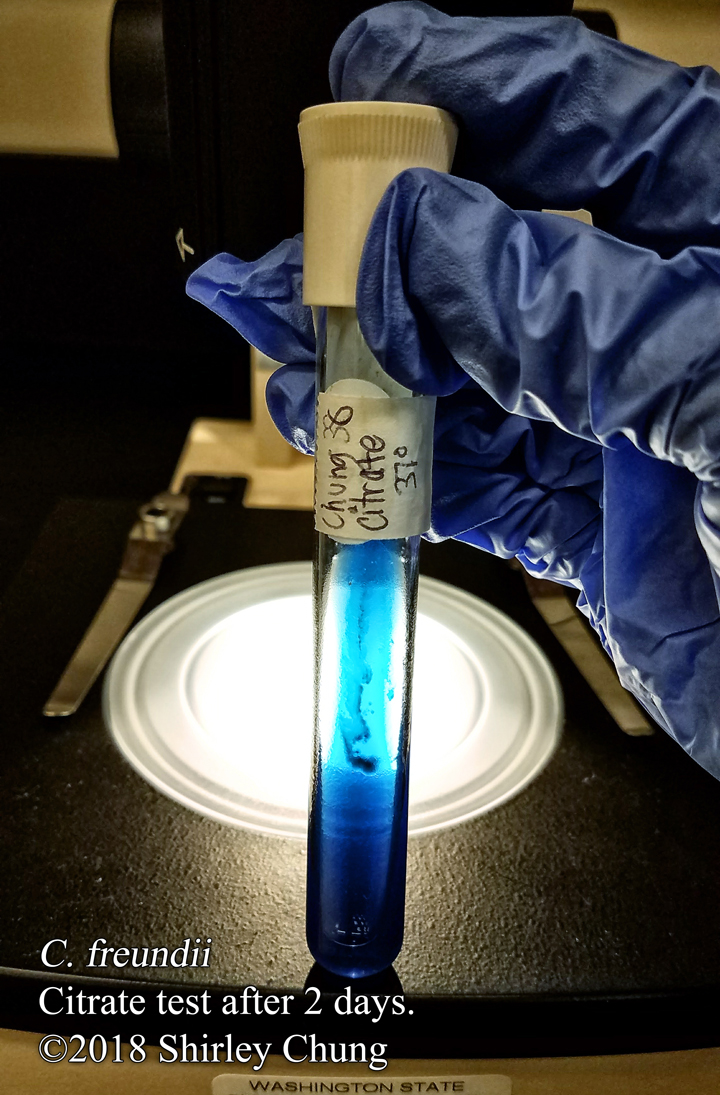
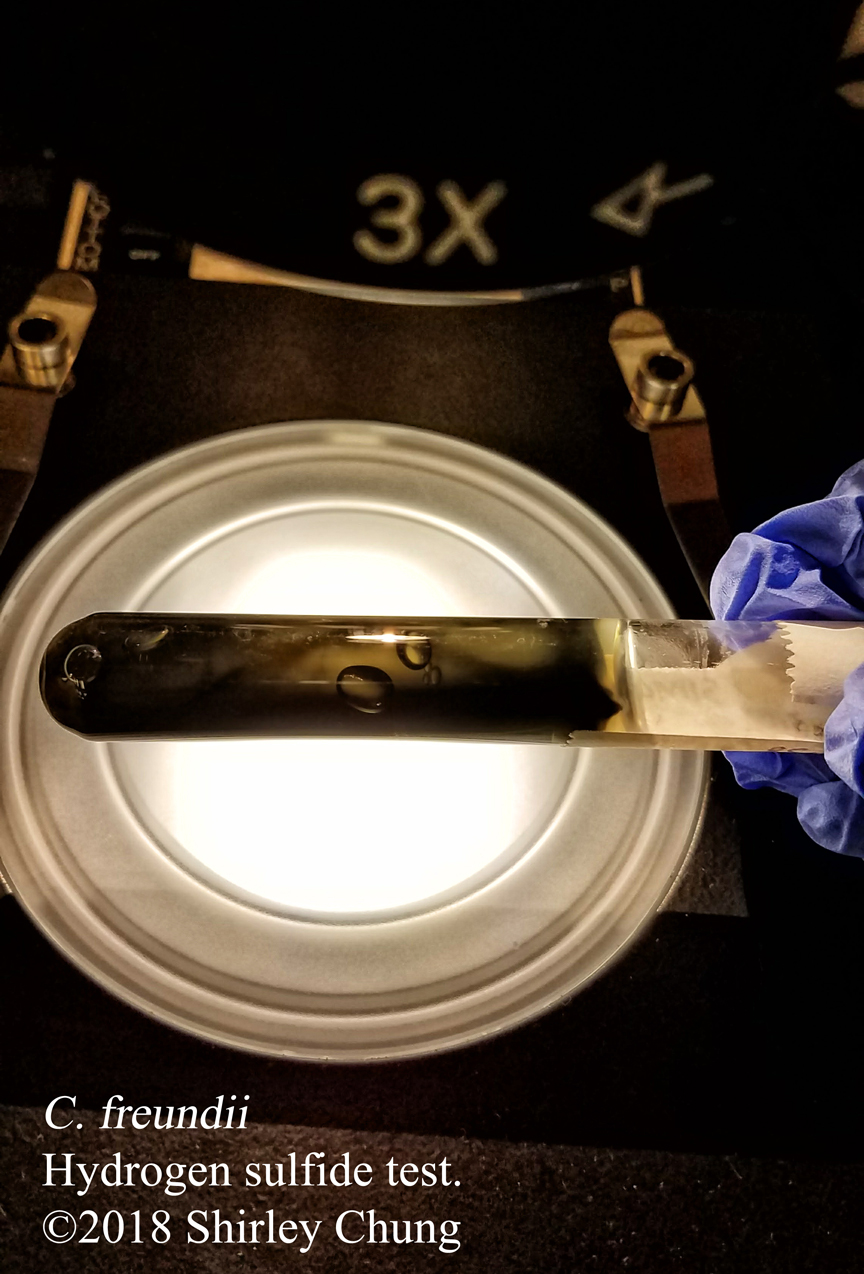
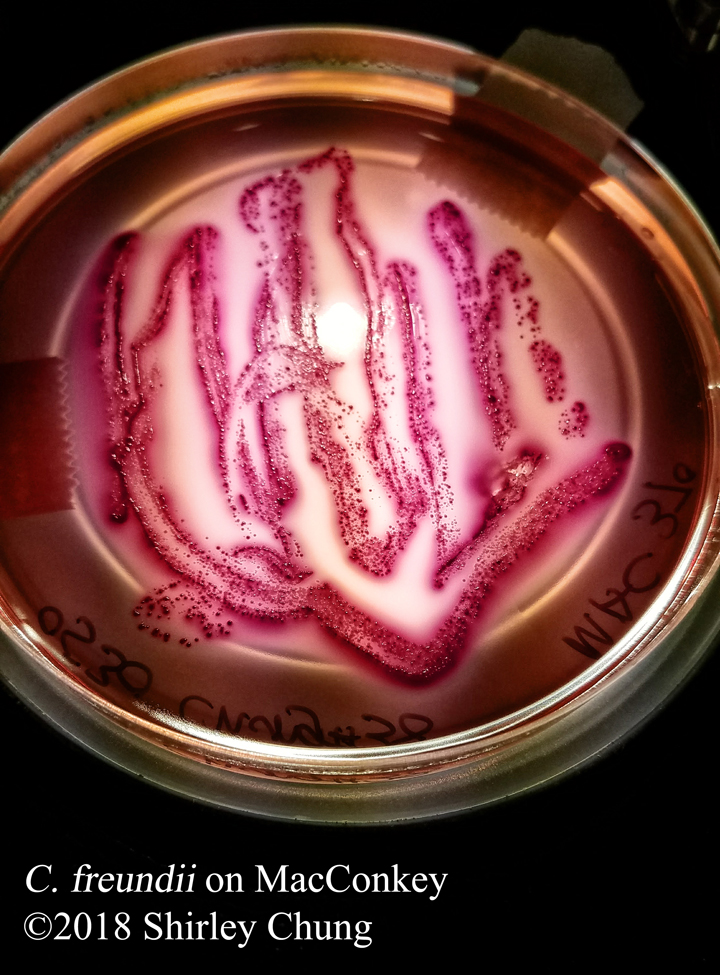
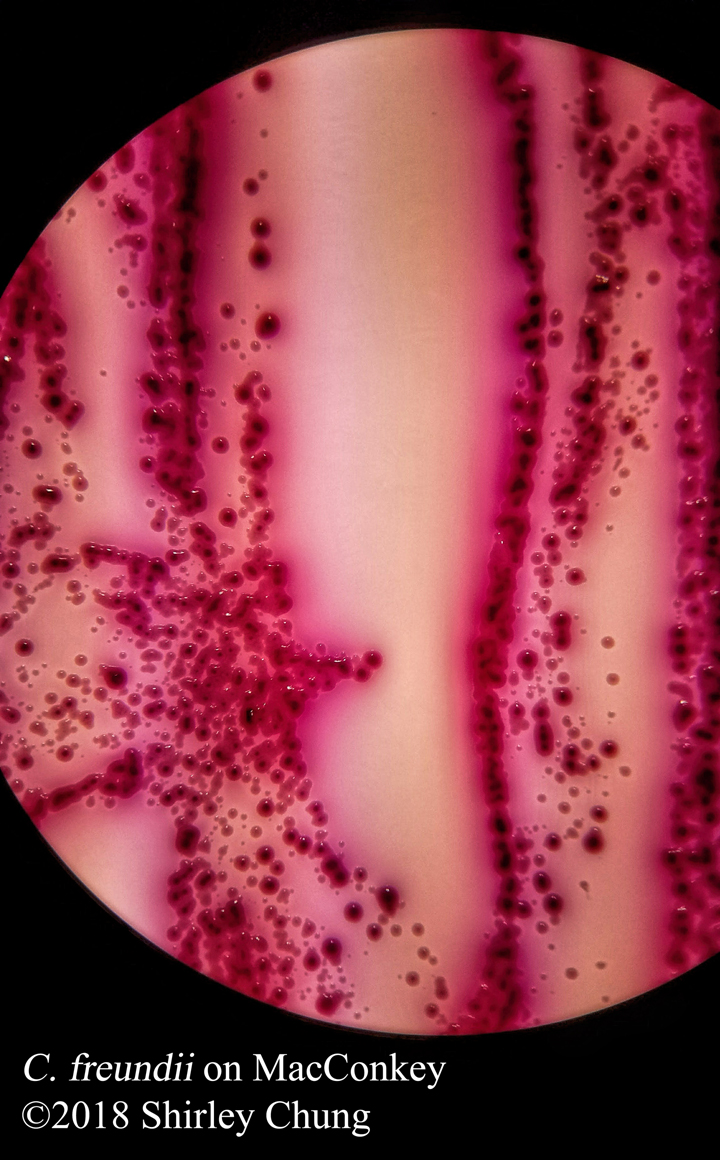
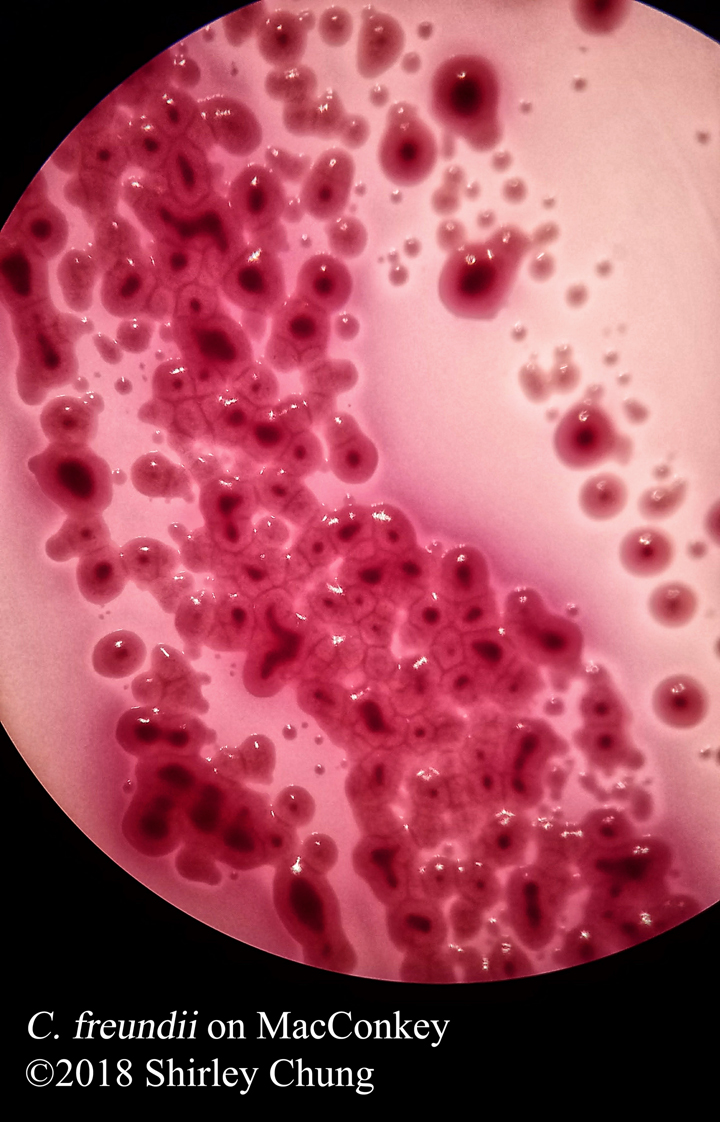
Simple stains: uses a single reagent (as opposed to multiple/contrasting reagents) to help distinguish between the organism and its background via boosting the contrast. Simple/basic stains help us to observe the morphological characteristics. Examples of simple stains: methylene blue, crystal violet, carbol fuchsin.
Clinical significance. Relatively quick and easily performed staining technique that aids in basic identification via morphological characteristics. Also helps to estimate the prevalence/proliferation of the organism.
Summary of procedure.
- Using aseptic technique at all times, prepare a smear & heat fix.
- Flood slide with
Methylene blue for 1-2 minutes, or
Crystal violet for 20-60 seconds, or
Carbol fuchsin for 15-30 seconds. - Using a bottle of deionized water, gently rinse the slide while holding the slide parallel to the stream of water.
- Very very gently blot (not wipe) slide using bibulous paper.
Reference
Cappuccino, J. G., & Welsh, C. (2018). Microbiology: A laboratory manual.