Anatomy & Physiology: Bones—Skull.
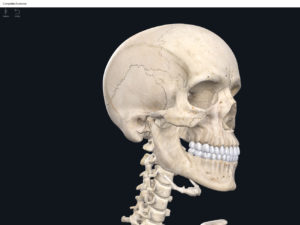
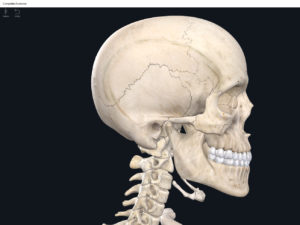
Structure.
Cranial bones: frontal bone, 2 parietal bones, 2 temporal bones, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone.
Facial bones: 2 nasal bones, 2 maxillae, 2 zygomatic bones, mandible, 2 lacrimal bones, 2 palatine bones, 2 inferior nasal conchae, vomer.
- Except for the auditory ossicles, the mandible is the only moveable bone of the skull.
- Sutures: immoveable joints that hold the skull together.
Function.
- Protects, supports, and stabilizes brain, sense organs, nerves, and vessels.
- Serves as attachment sites for muscles and membranes (meninges).
Clinical Significance.
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.