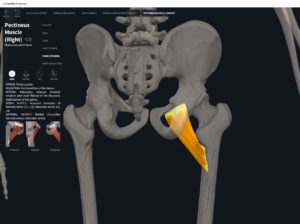
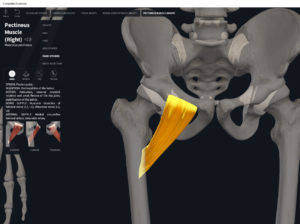
Anatomy & Physiology: Muscles—Pectineus.
Structure.
- Origin: pectineal line on the superior pubic ramus of pelvis.
- Insertion: pectineal line on the posterior surface of the upper femur.
Function.
- Concentric action: accelerates hip adduction, medial rotation.
- Reverse mover action: anterior tilt pelvis; ipsilateral rotation of pelvis.
- Eccentric action: controls/restrains/decelerates hip abduction, lateral rotation.
- Isometric action: stabilization of lumbo-pelvic hip complex.
- Innervation: femoral nerve.
- Arterial supply: femoral artery, deep femoral artery obturator artery.
Clinical Significance.
More.
- https://www.anatomynext.com/pectineus/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=noLowMVp7dc
- https://www.nielasher.com/blogs/video-blog/trigger-point-therapy-treating-pectineus
- https://www.body-n-muscles.com/2016/11/pectineus.html
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Clark, M., Lucett, S., Sutton, B. G., & National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2014). NASM essentials of corrective exercise training. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.