Download these notes.
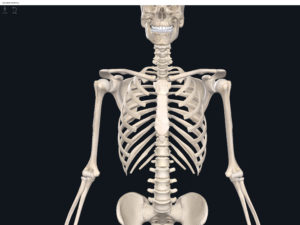
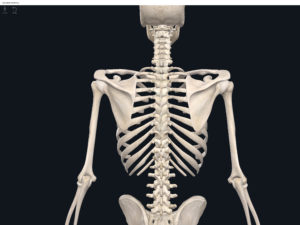
Anatomy & Physiology: Bones—Lumbo-Pelvic Hip Complex (Pelvic Girdle).
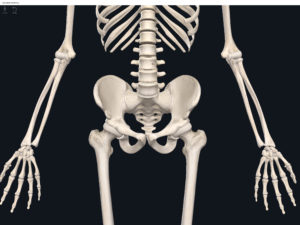
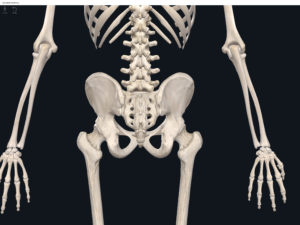
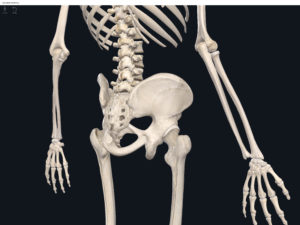
Structure.
- The lumbo-pelvic hip complex (LPHC) is a keystone structure in the human body as it transmits forces up through the lower kinetic chain to the upper kinetic chain.
- The LPHC consists of: 2 coxal (hip) bones joined anteriorly at the pubic symphasis; the sacrum; and the coccyx.
- Sacroiliac joint: where the auricular surface of the ilium articulate with the auricular surface of the sacrum.
- Coxal bone (hip bone): consists of 3 bones (initially separated by cartilage but fuses together around age 23 yrs): ilium, pubis; ischium (“Your hip is I.P.I. or ippy”).
- Ilium: superior and largest of the hip bones.
- Ala (“wing”).
- Acetabulum: forms part of the hip socket.
-
- Iliac crest: superior border, extending anteriorly to form the anterior superior iliac spine. Palpateable.
- Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS): palpateable landmark.
- Anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS): palateable landmark.
- Posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS): palpateable landmark.
- Posterior inferior iliac spine (PIIS): palpateable landmark.
- Greater sciatic notch: inferior to the PIIS, through which the sciatic nerve passes (sciatic nerve is longest nerve in human body).
- Iliac fossa.
- Auricular surface: roughened area and articulates with the auricular surface of the sacrum to form the SI joint.
- Arcuate line.
- Posterior gluteal line (lateral surface).
- Anterior gluteal line (lateral surface).
- Inferior gluteal line (lateral surface).
- Ischium: inferior and posterior portion of the coxal bone.
-
- Ramus: fuses with the pubis.
- Ischial spine.
- Lesser sciatic notch.
- Ischial tuberosity: rough and thickened area.
- Obturator foramen: formed from the ischium and pubis. Largest foramen in the skeleton. Almost totally closed off by fibrous obturator membrane.
- Pubis: inferior and anterior portion of the coxal bone.
- Superior ramus.
- Inferior ramus: the inferior rami of the two coxal bones, form the pubic arch.
-
- Pubic tubercle.
- Pubic crest.
- Pubic symphasis: joint between two hip bones with fibrocartilage inbetween. In pregnant women, relaxin (hormone) increases the flexibility of the pubic symphasis.
- Obturator foramen.
- Acetabulum: hip socket of hip joint formed by ilium, ischium, and pubis.
- False vs. True Pelvis.
- Pelvic brim: defines the superior and inferior pelvis. Higher posteriorly than anteriorly due to tilt.
- False pelvis: the portion of the pelvis superior to the pelvic brim.
- True pelvis: the portion of the pelvis inferior to the pelvic brim.
- Pelvic inlet: superior opening of the true pelvis.
- Pelvic outlet: inferior opening of the true pelvis.
- Pelvic axis.
- Male pelvis: tend to be larger, heavier, with more surface markings.
- Female pelvis: tend to be shallower and wider, more spacious true pelvis.
Function.
Clinical Significance.
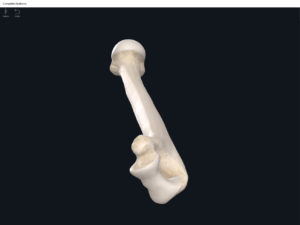
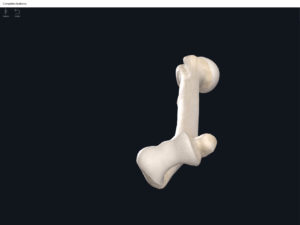
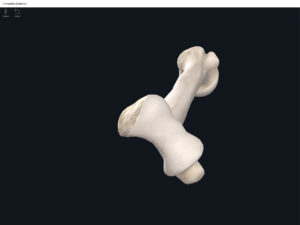
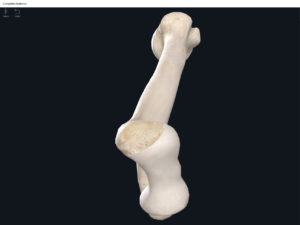
Lumbo Pelvic Hip Complex, LPHC. Used with permission by 3D4Medical.
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Cedars-Sinai. (2018). Vertebrae of the spine. Retrieved from https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/v/vertebrae-of-the-spine.html
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.