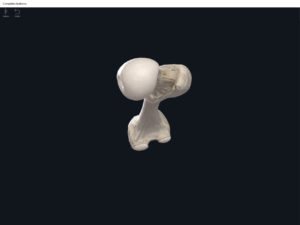
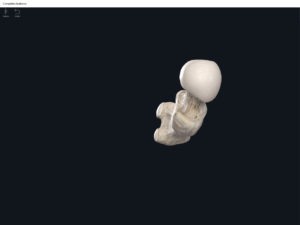
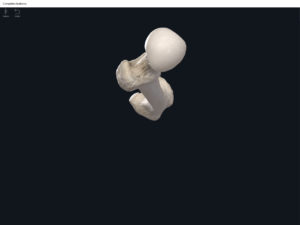
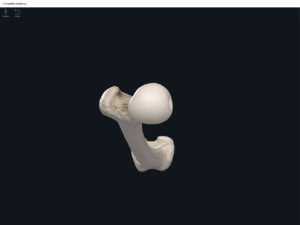
Anatomy & Physiology: Bones—Femur.
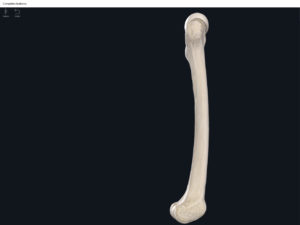
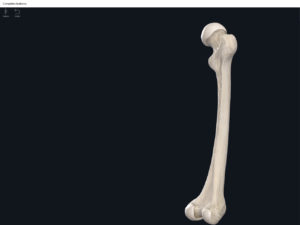
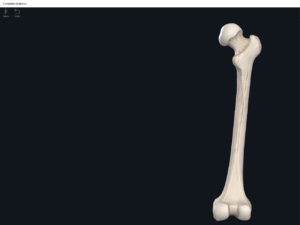
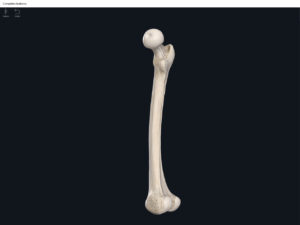
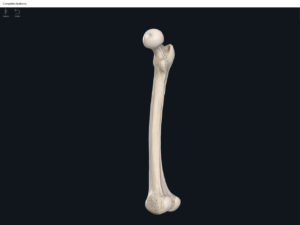
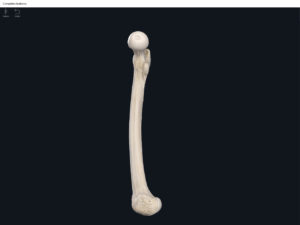
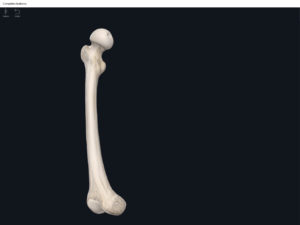
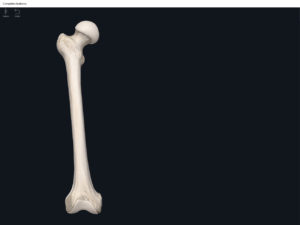
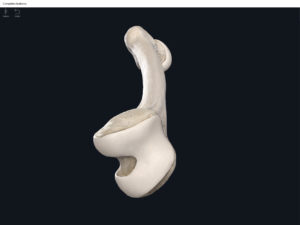
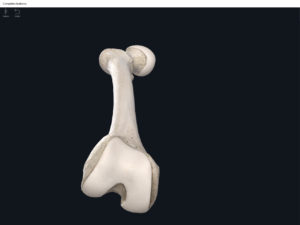
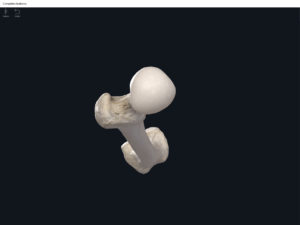
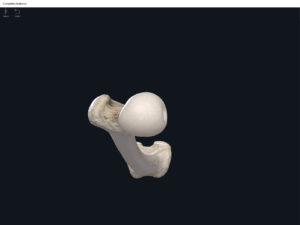
Structure.
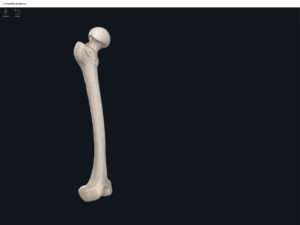
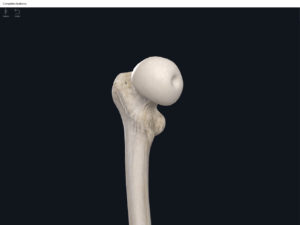
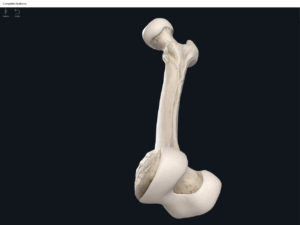
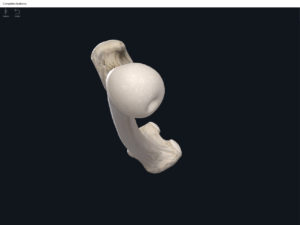
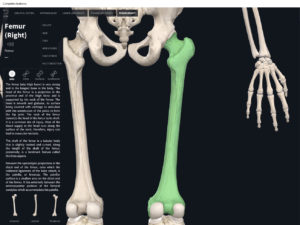
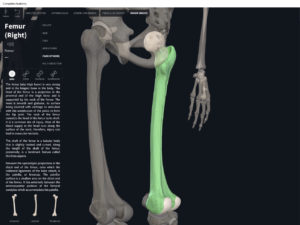
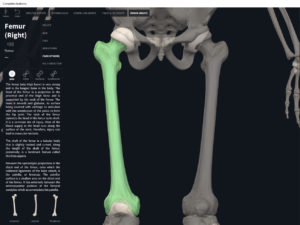
- The largest, longest, strongest, and most massive bone of the body.
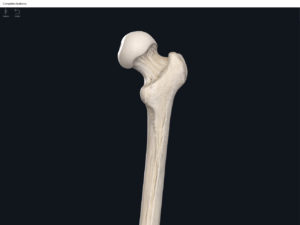
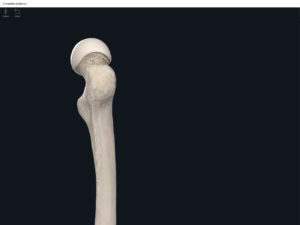
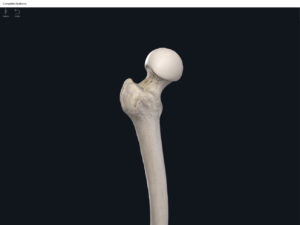
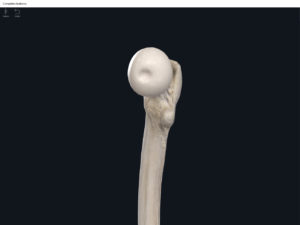
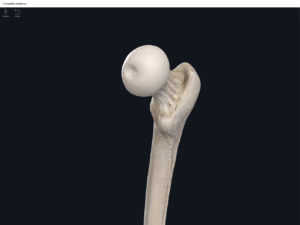
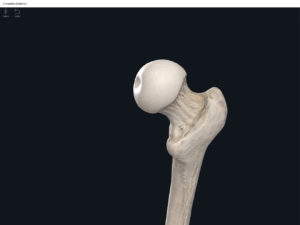
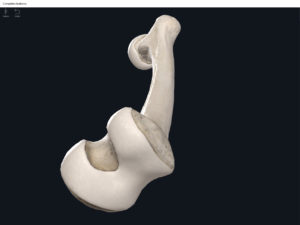
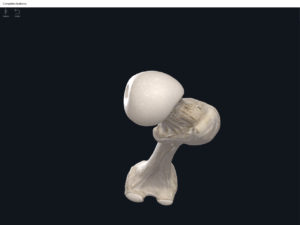
- Head: articulates with the acetabulum of the LPHC (lumbo-pelvic hip complex).
- Fovea capitis: a dimple-like depression on the femoral head.
- Greater trochanter: prominence that is observeable and easily palpateable.
- Lesser trochanter.
- Interotrochanteric line: anterior line between the two trochanters.
- Interotrochanteric crest: posterior line between the two trochanters.
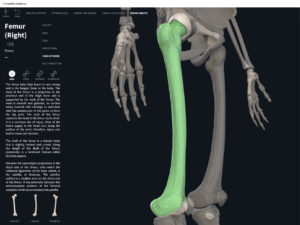
- Gluteal tuberosity.
- Linea aspera.
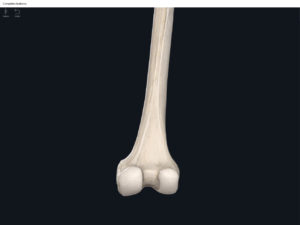
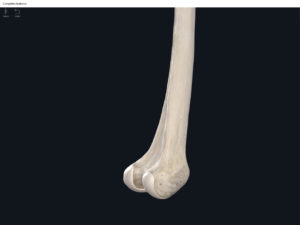
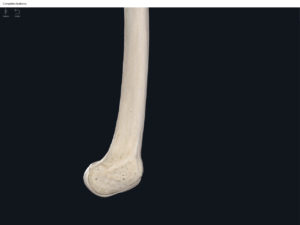
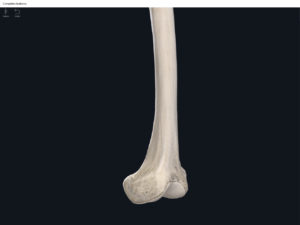
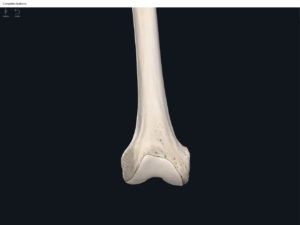
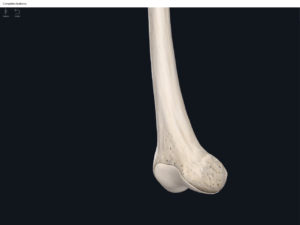
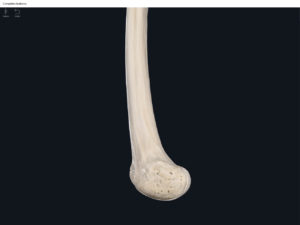
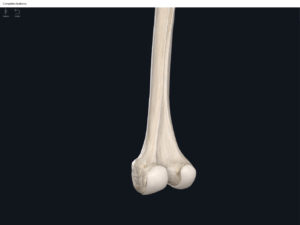
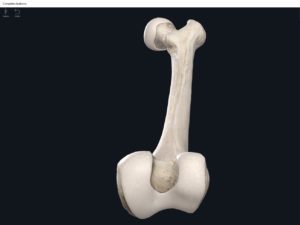
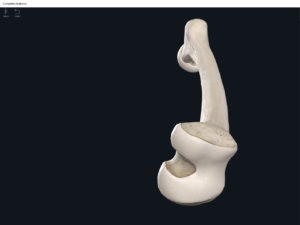
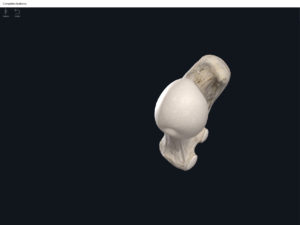
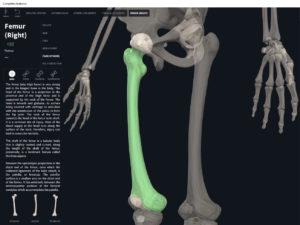
- Media condyle.
- Lateral condyle.
- Medial epicondyle: superior to the condyles.
- Lateral epicondyle: also superior to the condyles.
- Intercondylar fossa: posterior surface; depression between the condyles.
- Patellar surface: anteriorly; a smooth area to allow for patella movement.
Function.
Clinical Significance.
- Greater trochanter: Landmark for intramuscular injections.
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Cedars-Sinai. (2018). Vertebrae of the spine. Retrieved from https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/v/vertebrae-of-the-spine.html
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.