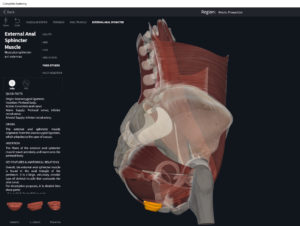
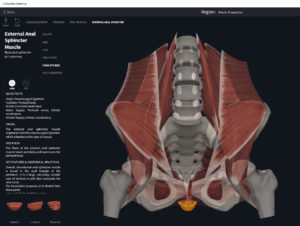
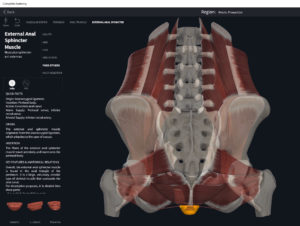
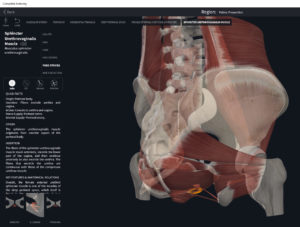
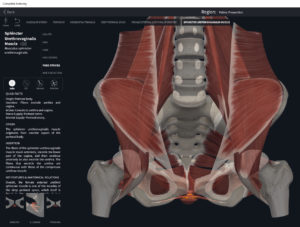
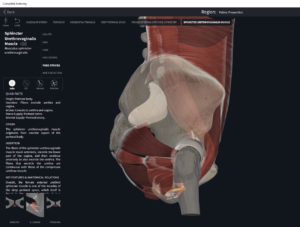
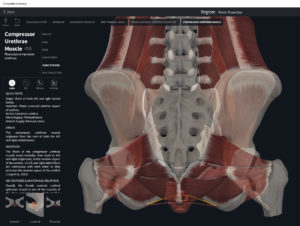
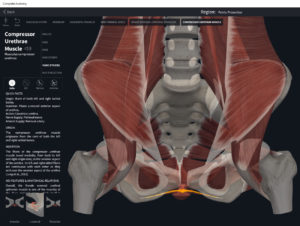
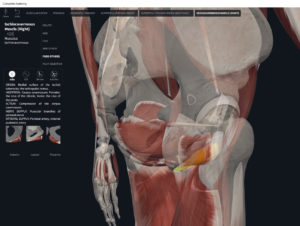
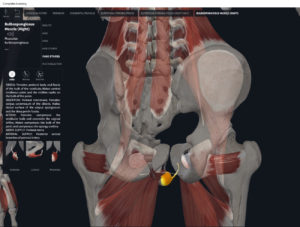
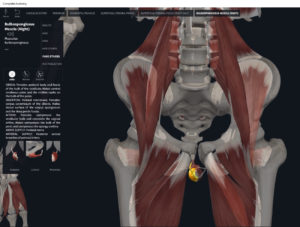
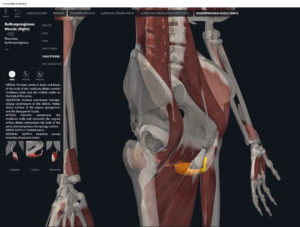
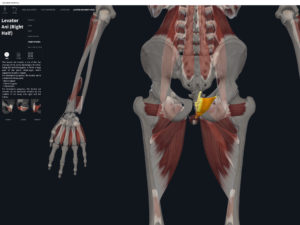
Structure.
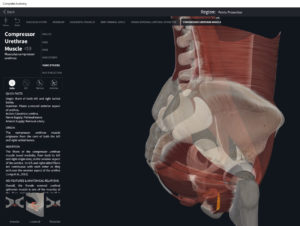
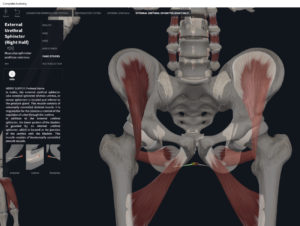
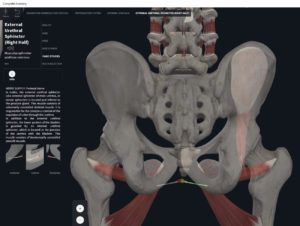
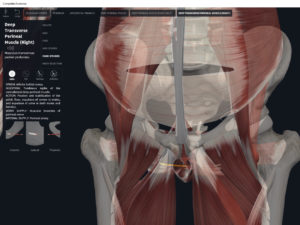
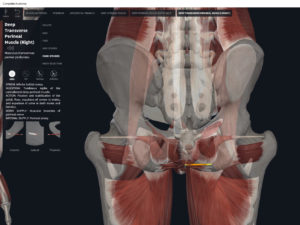
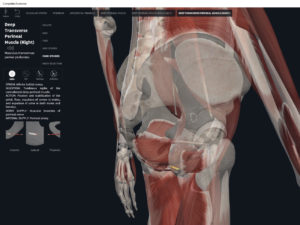
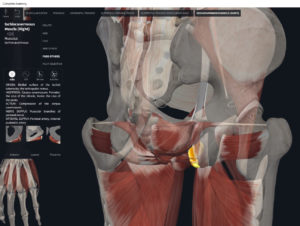
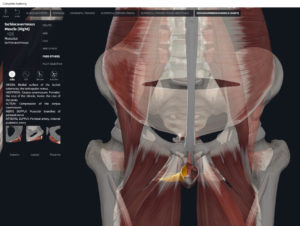
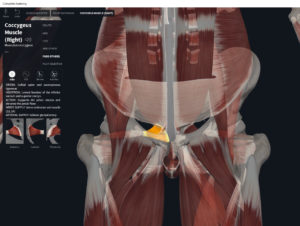
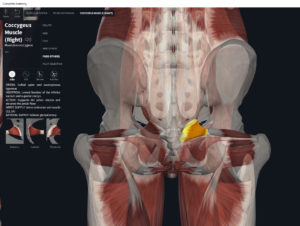
- Origin: anococcygeal ligament.
- Insertion: perineal body of perineum.
- Spans above and below the pectinate (dentate) line.
Function.
- Concentric action: keeps anal canal and anus closed.
- Isometric action:
- Innervation: sacral spinal nerve S4 and inferior rectal branch of pudendal nerve.
- Arterial supply: superior rectal artery, contributions from middle rectal and median sacral arteries (above dentate line); inferior rectal artery from internal pudendal artery (below dentate line).
Clinical Significance.
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Clark, M., Lucett, S., Sutton, B. G., & National Academy of Sports Medicine. (2014). NASM essentials of corrective exercise training. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.