(Work in progress).

Pre-Lab Questions.
- What is the purpose/function of the saturated NaCl (aq)?
- What is the purpose/function of the anhydrous sodium sulfate?
- What is the purpose/function of the dichloromethane?
- In the separatory funnel, which layer is the aqueous layer and which layer is the organic layer?
- What is the density of water vs. dichloromethane?
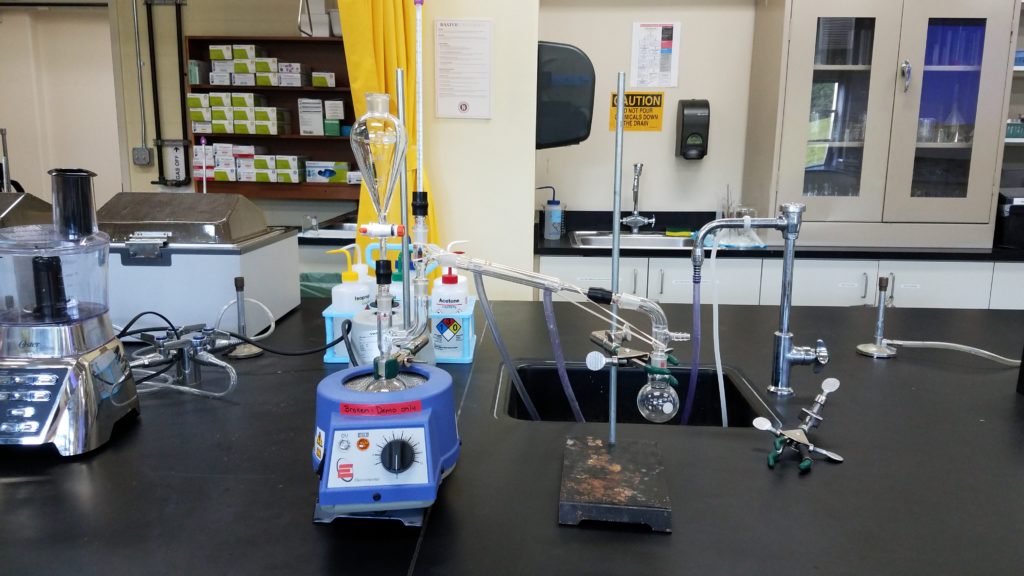
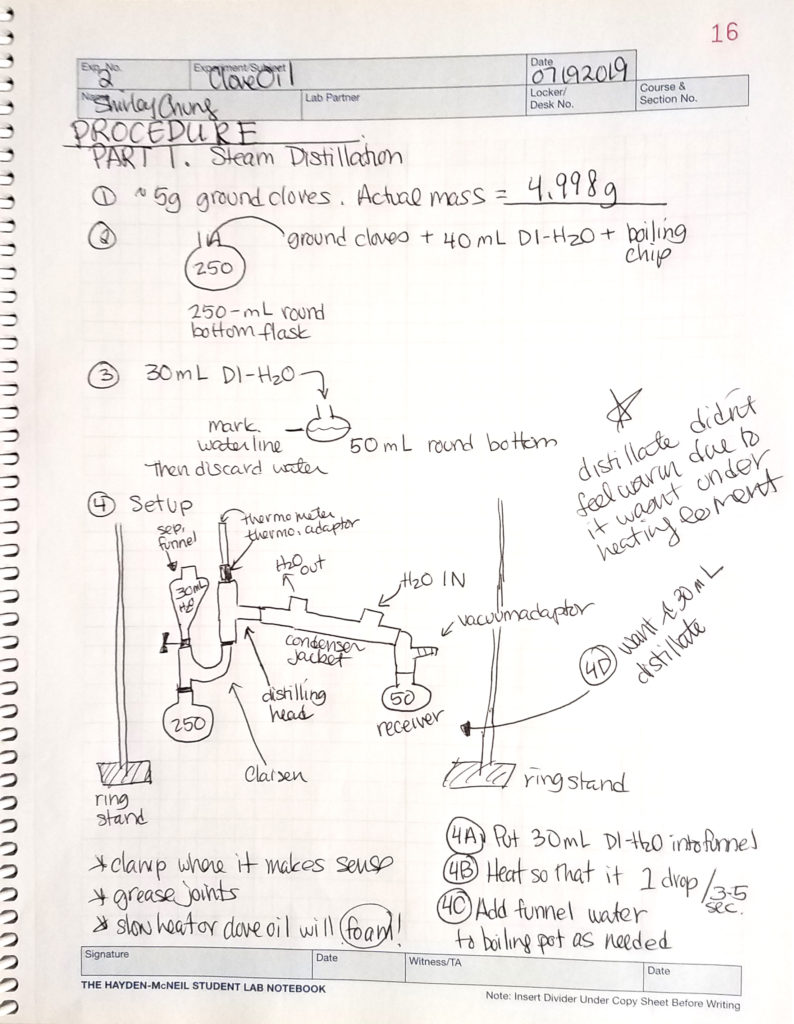
Materials and Methods. Clove oil was extracted from ground cloves in three major processes: steam distillation; crude oil extraction; and product purification.
Steam distillation. Ground cloves were boiled in closed, horizontal, simple steam distillation setup (round-bottom boiling flask, Claisen tube, distilling head, water condenser, vacuum adapter, small separatory funnel to renew the water supply, and receiving flask) which yielded 30 mL of distillate.
Crude oil extraction. The distillate was transferred to a separatory funnel. Saturated NaCl solution was added to the distillate to “pull” the aqueous layer out as a diluent for the NaCl (aq). To further separate the aqueous and organic layers, the distillate was washed with a small amount of dichloromethane and then shaken vigorously (venting frequently). Upon settling, the denser organic layer was drained from the separatory funnel into an Erlenmeyer flask. This process was repeated 3 times. This crude extraction was based on the principle: “like dissolves like” or “like is miscible in like”.
Oil purification. Anhydrous Na2SO4 was added to the crude oil (repeated if necessary) to absorb any remaining water. When the mixture looked “granular” or turbid, the dried dichloromethane/organic solution was transferred to a pre-weighed boiling flask (boiling chip inside). A rotary evaporator removed the rest of the dichloromethane leaving a purified clove oil product.







Resources:
