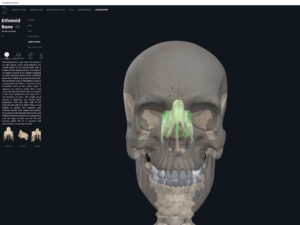
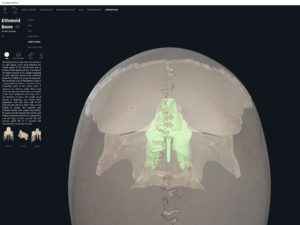
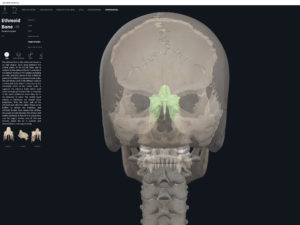
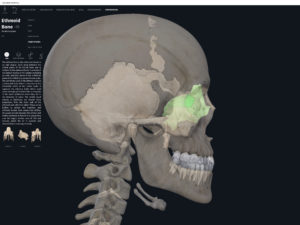
Anatomy & Physiology: Bones—Skull, Fontanels.
Structure.
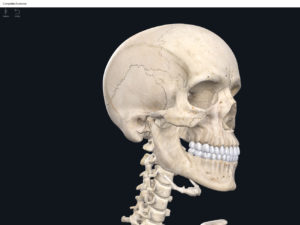
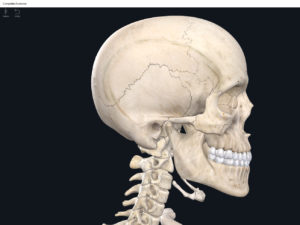
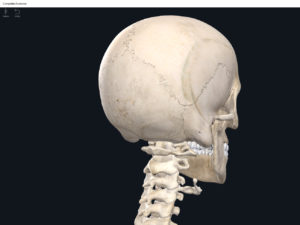
- The skull of developing embryo through birth is not fully developed.
- Gaps between skull bones are cartilage and mesenchme which will be ossified later.
- These gaps are called fontanels (i.e. the “soft spots”).
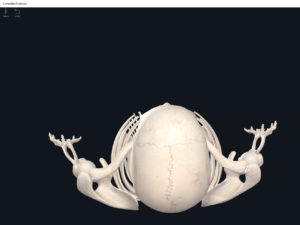
- Anterior fontanel: midline between the two parietal bones and frontal bone. Closes 18-24 months after birth.
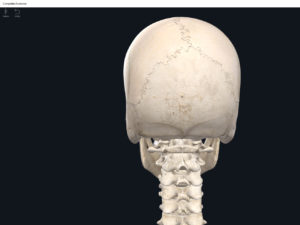
- Posterior fontanel: midline between the two parietal bones and the occipital. Closes 2 months after birth.
- Anterolateral fontanel: between the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal bones. Closes 3 months after birth.
- Posterolateral fontanels: bilaterally, between the parietal, occipital, and temporal bones. Closes 12 months after birth.
Function.
Clinical Significance.
References
Biel, A. (2015). Trail guide to the body: A hands-on guide to locating muscles, bones and more.
Jenkins, G., & Tortora, G. J. (2012). Anatomy and Physiology: From Science to Life, 3rd Edition International Stu. John Wiley & Sons.
Muscolino, J. E. (2017). The muscular system manual: The skeletal muscles of the human body.